

You will need to copy the following line as the first line of the file Luckily it is quite easy and the startup script can be opened for editing from the server view from the last step.Ī text file will open. You would need to manually edit the startup script of the server.
#Jrebel weblogic update#
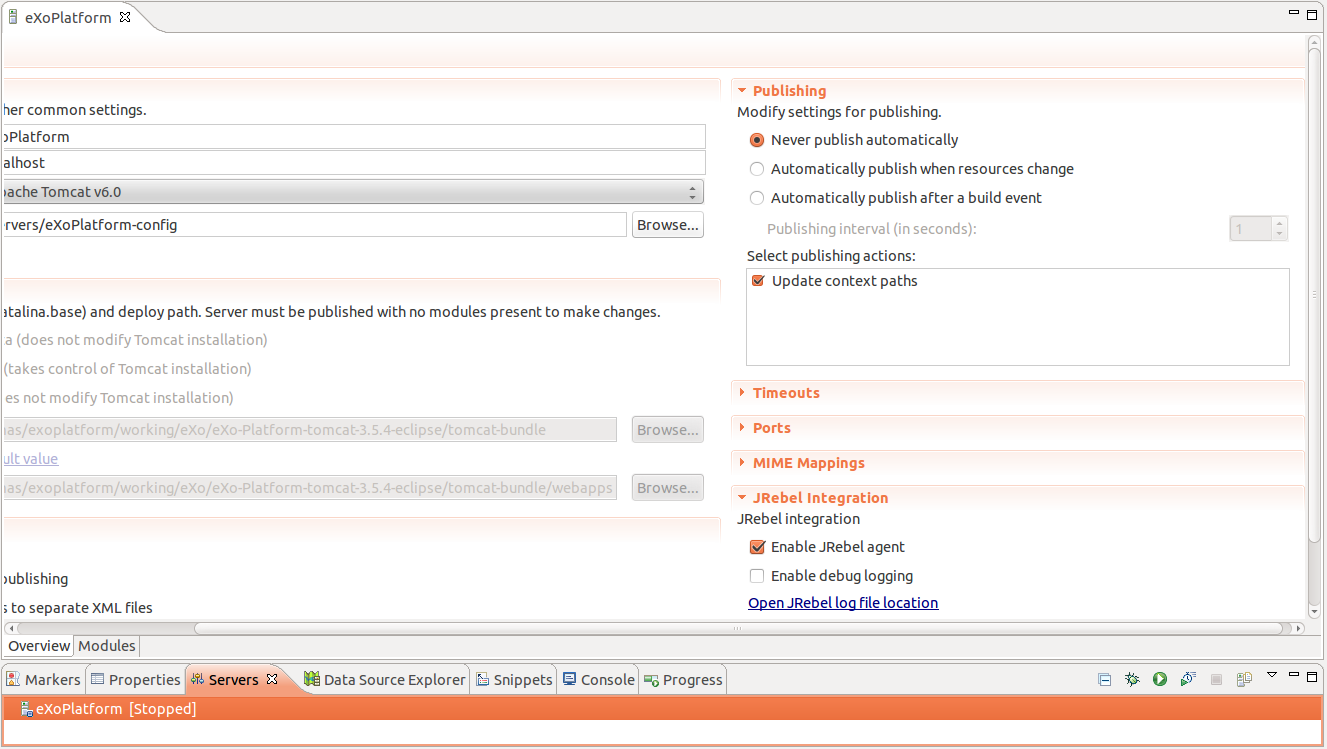
Until we update our JRebel Eclipse plugin you have to manually enable JRebel for the Weblogic Server. STEP 4a: Configuring the Eclipse WTP IDE workaround NB! With the current version of the Eclipse JRebel plugin checking the checkbox does NOT WORK. Open JRebel Integration and check Enable JRebel agent. It may seem wrong to disable automatic publishing, but as JRebel will take care of updates from now on, it would just slow you down. Open Publishing and choose Never publish automatically. Open the Servers View and double click the BEA WebLogic Server that your application is deployed to (if you don’t see the Servers View go to Window » Show View » Servers). You may skip this step if you run Weblogic outside of the Eclipse IDE. If your project is one of the exceptions, edit the file manually as described in the Installation manual, otherwise generate the rebel.xml like this:Ĭlick on your project and pick Generate rebel.xml In these cases, the JRebel Eclipse IDE plugin can generate the rebel.xml file for you, on a per project basis. In 99% of cases, people tend to use one module per project. If you use Maven you can use the JRebel Maven plugin that will generate the rebel.xml in accordance with the module pom.xml as described in the Maven Plugin configuration manual. Put it in the root of a source or resource folder in your project (the same place where the. The rebel.xml configuration file should be placed in your WEB-INF/classes directory in the case of a web module and in the jar root in the case of an ejb module. You’ll need to have one rebel.xml file per module. This is mandatory when you deploy your app as a WAR/EAR. We’ll use a rebel.xml configuration file to tell it. In order to do it’s magic, JRebel needs to know where your classes and resources are. STEP 3: Make a rebel.xml for your application
#Jrebel weblogic install#
You can install the plugin by going to Help » Software updates » Available software » Add site and use the URL as the update site. The JRebel Eclipse IDE plugin was introduced with JRebel 2.0 and makes configuring and using JRebel considerably easier. STEP 2: Installing JRebel Eclipse IDE plugin The latest stable version of JRebel can be downloaded here.

Configuring the Eclipse WTP IDE workaround.STEP 4: Configuring the Eclipse WTP IDE.STEP 3: Make a rebel.xml for your application.STEP 2: Installing JRebel Eclipse IDE plugin.Most of the steps will be applicable to other versions as well, but it may look different from the screenshots included. This tutorial assumes that you are using Eclipse 3.x (with Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse installed) with WebLogic 9.x or later.
#Jrebel weblogic how to#
In this tutorial we explain how to install and use it step-by-step.įirst, take a quick look at how coding looks when using JRebel ( formerly JavaRebel). JRebel reduces this time by 80%, so it’s worth taking a few minutes to try it out. To extrapolate a bit, that’s ~13 minutes per hour of coding, adding up to ~256 hours or 6.4 full work weeks annually.
In a recently conducted survey (with 1100+ respondents), WebLogic users estimated spending approximately 21% of all their coding time on the redeployment process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
